- Resources
Problem Gambling Prevention Professionals
What is Problem Gambling?
Problem Gambling is gambling behavior that is damaging to a person or their family, often disrupting their daily life and career. Anyone who gambles can be at risk for developing a gambling problem. (National Council on Problem Gambling).
What is Problem Gambling Prevention?
Problem gambling prevention is the systematic effort to reduce the onset and impact of gambling-related harms through education, health promotion, responsible gambling practices, and early identification of risk. It draws on the same foundations used across behavioral health, including strengthening protective factors, reducing risk factors, engaging communities, and shaping environments to limit exposure to high-risk gambling.
Continuum of care
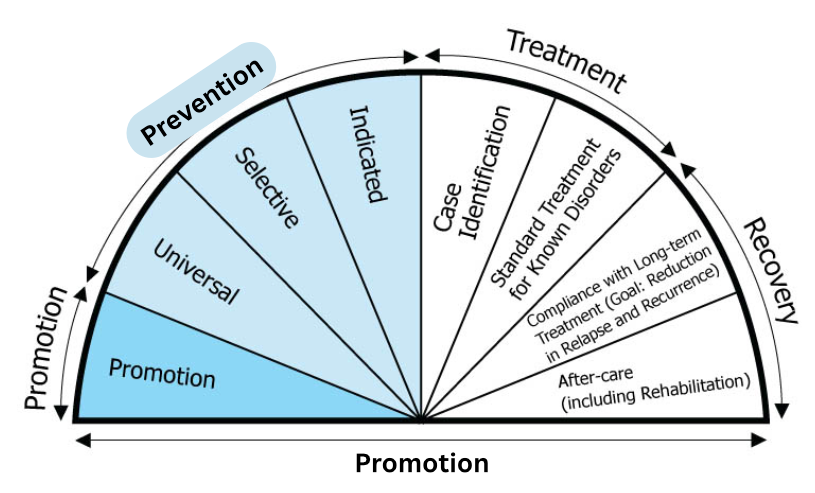
Prevention plays a critical role in the continuum of care. There are three levels of prevention.
Universal prevention involves interventions delivered to the general public, regardless of individual risk such as public campaigns or education in classrooms on gambling awareness.
Selective prevention involves interventions delivered to groups identified as being at greater risk than the general public. Examples include targeted school-based prevention programs and interventions for high-risk populations such as athletes or those engaged in substance use or mental health treatment.
Indicated prevention involves interventions delivered to individuals experiencing early warning signs of gambling-related harm, including tabling activities on-site at a casino/racino or lottery retailer with promotion of referrals and resources for problem gambling support services.
Continuum of gambling
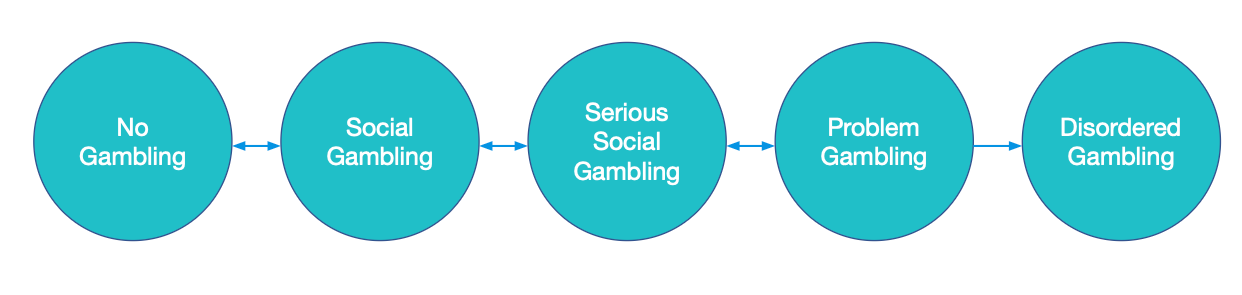
Gambling exists on a continuum ranging from no gambling to disordered gambling. No gambling is when a person does not engage in any form of gambling. Social gambling is gambling at irregular intervals for the purpose of entertainment. Someone who engages in social gambling has the ability to set limits on how much money and time they spend gambling. Serious social gambling is gambling regularly for entertainment. Problem Gambling refers to a pattern of gambling behavior that disrupts a person’s life but may not meet the full criteria for a clinical diagnosis. Gambling disorder is a more severe, clinically diagnosable condition where the person is unable to stop gambling despite its harmful effects.
Opportunities for applying prevention strategies are encouraged for individuals at different stages on the gambling continuum. For those who do not gamble, prevention efforts can focus on education about the risks of gambling and building healthy, alternative recreational activities. For those who are social or serious social gamblers, prevention efforts can be focused on providing tips and strategies for responsible gambling, setting limits, and understanding the signs of risky behavior. For those experiencing problems, interventions can include providing strategies on how to reduce harm from gambling behaviors, including brief interventions related to limit setting, responsible gambling, support groups or resource sharing. Individuals who have been identified as having a gambling disorder should be referred to specialized treatment.
when does gambling become a problem?
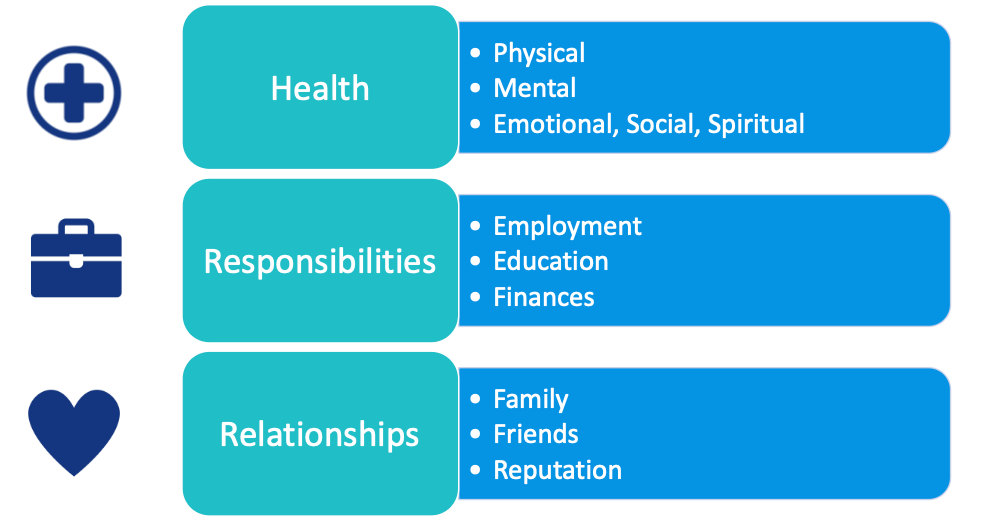
Gambling is a problem when it impacts a person’s health. This could look like a lack of sleep, stress, anxiety, depression, feelings of shame or worthlessness, high blood pressure, etc. It can also impact responsibilities resulting in missing work, school, not being able to focus on tasks, sports betting at work, etc. Problem gambling can impact relationships through financial problems, fighting over money, isolation, lying, etc.
problem gambling basics
Integrating prevention efforts

In 2025, PGNO launched its inaugural Problem Gambling Prevention Fellowship, bringing together prevention professionals from across Ohio to address a common challenge in the field: how to meaningfully integrate problem gambling prevention into the work already happening in communities every day.
Before developing this tool, the Fellows created and distributed a statewide survey to prevention professionals to better understand real world experiences, needs, and barriers related to integrating problem gambling into existing prevention efforts. The feedback and insight gathered from professionals across Ohio directly informed the development of this resource.
One of the tools created through this Fellowship is the Problem Gambling Integration Rack Card. Developed by prevention professionals for prevention professionals, this resource provides a practical starting point for understanding what problem gambling is and how it connects to existing prevention roles, outreach efforts, and community initiatives.
The rack card offers clear, accessible integration ideas for professionals working in general prevention, school based prevention, coalition work, and community engagement. It was designed to remove the guesswork and help professionals see that problem gambling prevention is not separate from their work, but something that can be naturally and effectively woven into what they are already doing.
This tool reflects both the real world expertise of Ohio’s prevention workforce and the collective insight shared by professionals across the state, serving as an easy reference for anyone looking to strengthen their ability to reduce gambling related harm in their community.

